Before the submission
Register, then sign in
The first requirement to submit data to HarnesstomDB is to be logged in. Only logged users with user account will be able to access certain functionality of the database through the web-application. If you are not already registered, you must create an account. To do so, please click on the login button at the right part of the Harnesstom gateway and then click on the new around here ?

To create an account, it is necessary to fill the registration form and accept the terms of use.
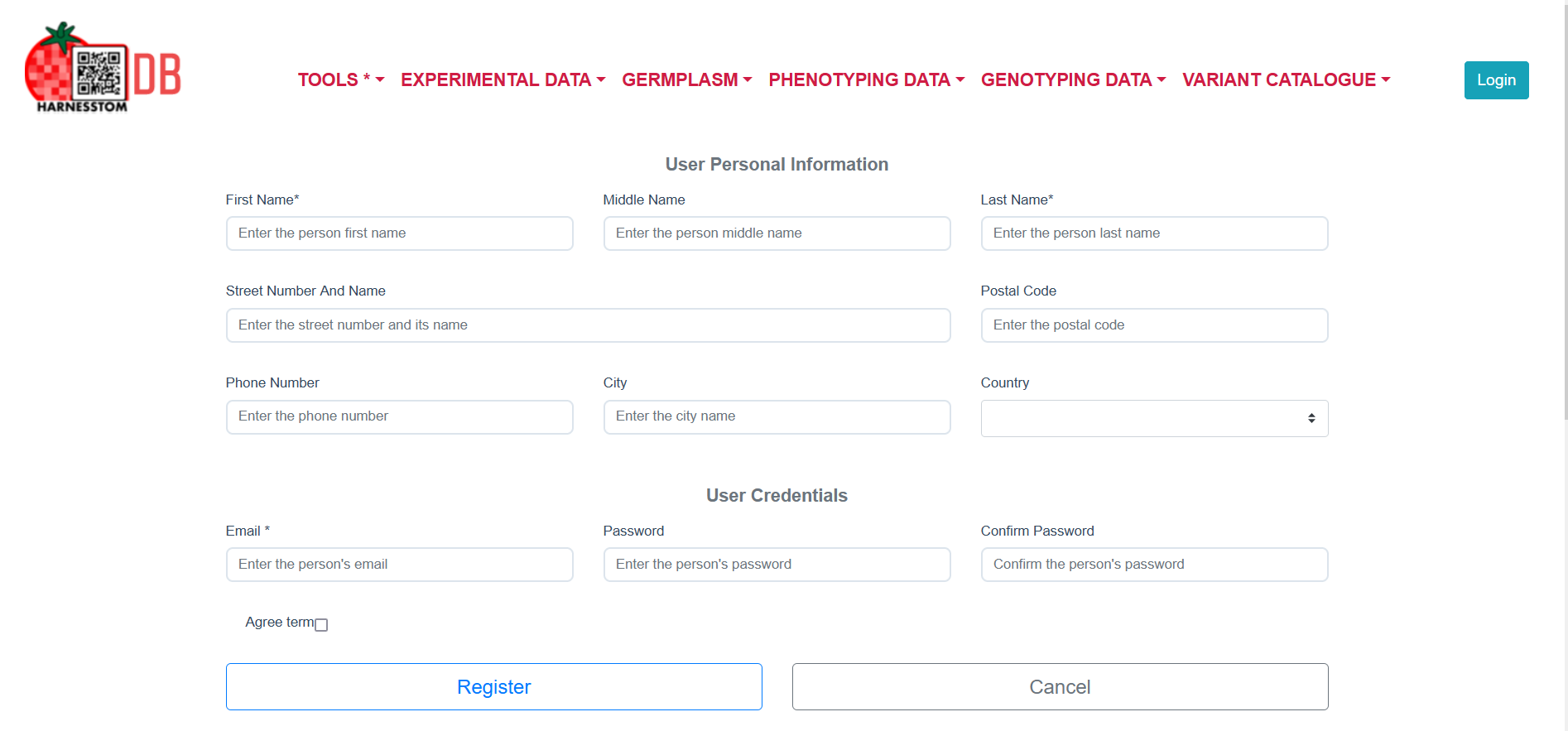 After filling out the registration form you should receive an account confirmation email from
noreply-emailverif@harnesstom.eu to validate your account.
Once your account has been confirmed, you can login to the website.
After filling out the registration form you should receive an account confirmation email from
noreply-emailverif@harnesstom.eu to validate your account.
Once your account has been confirmed, you can login to the website.
All registered users have permissions to submit, edit and update their own data, and download public HarnesstomDB data.
Accounts are only needed if you want to submit or download data
What data can be submitted ?
HarnesstomDB accepts curated data and metadata from germplasm collections and from different projects related genotyping, phenotyping, GWAS and QTL experiments as well images.
HarnesstomDB archives only curated data, raw data files should be submitted to specialized public repositories propriate to your field of study. You can use FAIRsharing registry to find an appropriate repository for your raw data.
We currently don't accept transcriptomics data, please submit it to TomExpress or other transcriptomic databases.
How to submit data ?
DB provide two options for submitting data. Manual entry through the HarnesstomDB v1.0 create application or bulk file submission using the HarnesstomDB v1.0 submission tool. The best option depends on the quantity of data you want to submit. The HarnesstomDB v1.0 create application is the best choice if you have a few records to submit. The HarnesstomDB v1.0 submission tool is the best option if you have many records to submit. You can combine both options.
To facilitate submission, we have created a guide to submit data using the HarnesstomDB v1.0 create application and an excel template HarnesstomDB template v1.0 October 2022 for bulk submissions. Before submitting to HarnesstomDB v1.0, we encourage all HarnesstomDB users to read the guide to understand the key HarnesstomDB concepts and familiarize yourself with the different forms available for data submission.
Please, feel free to contact us if you have doubts of problems with submission. Write a brief description of the type of data you are trying to submit, and one of our curators will quickly get back to you.
What do I need to prepare ?
To submit data to HarnesstomDB v1.0 all you need is to collect metadata describing your experiment and the files containing the datasets. In HarnesstomDB some fields are mandatory, therefore can't be empty. Other fields are optional, but greater detail will enhance the quality and the available information in the database.
Use the controlled vocabulary when required, the standard notations and accepted file formats. Please see Definitions and standards, Controlled vocabulary and accepted file formats. The table below outlines what metadata and data should be submitted through each for each type of experiment.

HarnesstomDB schema
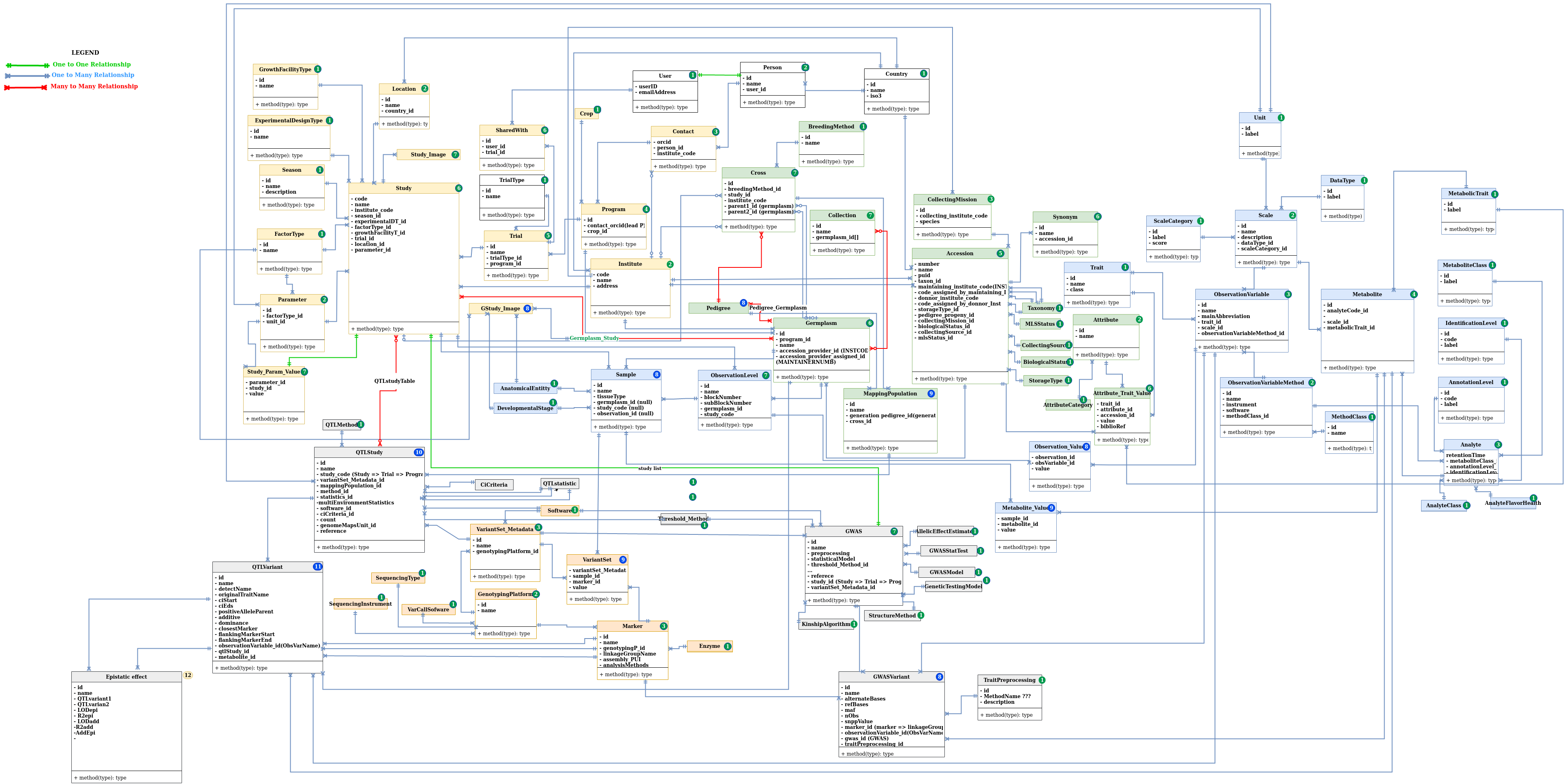
Before submitting data, it is important to understand how HarnesstomDB is organized. This will determine what you need to submit.
HarnesstomDB contains several modules conformed by metadata, controlled vocabulary and data tables interconnected between them by the ID assigned to each object when inserted into the database
- Experimental metadata core module
- Germplasm module
- Phenotyping module
- Genotyping module
- Variant catalogue
What is the experimental core metadata module?
The experimental metadata module stores the minimal information required to describe an experiment. Tables in this module are organized by a hierarchical relationship (Crop, program, trial, study).
-
• CROPS:
this table contains the common crop name associated with the data stored in the database
(a crop includes the cultivated species and its wild relatives).
HarnesstomDB is prepared to store data and metadata from multiple crops in separate sub-databases.
• PROGRAMS:
programs are research projects with defined aims associated with a crop. They can exist at various scales
(for example, they could encompass a grant-funded programme of work with trials and studies or a breeding program).
Program contains basic information describing a program such as name, description and program leader. A Program can contain multiple Trials.
• TRIALS:
trials comprise single or multiple studies (e.g. multi location international trials) conducted to answer a particular biological question in a frame of a program.
They contain the information describing the trial such as to which program is associated, the type of trial (i.e agronomic trial, environmental exposure trial),
the name and its abbreviation, a short description, the start and end data, associated publications, permanent unique identifier (if data is submitted to any public repository),
date of public release of this trial, License for reusability of the data associated with this investigation and the persons authorized by the submitter to use unpublished or non-public data.
• STUDIES:
A study is defined as an experiment conducted at a single geographic location to answer the defined question in a trial.
This contains minimal information to describe where and how the experiment was performed and the germplasm associated with the study.
It contains several associated tables with a controlled vocabulary to describe the experiment such as growth facility type, experimental design, factor type, parameters, season.
• CONTACTS:
List of program contacts (program leaders and other persons) related to the project (submitter, researcher…)
• INSTITUTES:
List of institutions associated a project, study and accessions
What is the germplasm module?
The germplasm module stores general information about the germplasm stored in the database. In HarnesstomDB, the germplasm term is the identifier of an accession in a program. The same accession can be used in different programs with different germplasm names. The same accession can be maintained in different institutions under different names. The main tables in this module are:
-
• GERMPLASM:
The name of the germplasm used in each program/trial and study, its donor and the donor accession number.
• ACCESSIONS:
Multicrop passport descriptors of the accessions used as germplasm in each program. It contains information related to the
name, the origin, the taxonomy, the maintaining, breeding and donor, institutes, the pedigree,
the status of an accession with regards to the Multilateral System (MLS) of the International Treaty on
Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture. Further, it contains additional information regarding to simply-inherited
characteristics inherent in the germplasm line (mutations, QTLs, phenotypes and any other remarkable information of interest for breeding).
• COLLECTIONS:
Subsets of germplasm of interest, created in the frame of a project, using specific criteria. For example, core collections.
• PEDIGREE:
Genetic relationship between germplasm, their parents and progeny, as result of breeding crosses.
• MAPPING POPULATIONS:
Mapping populations used in the different projects/ trials or studies
What is the phenotyping module?
The phenotyping module stores metadata associated to the traits studied, the germplasm phenotyped in each study (at macromolecular or molecular scale) and the phenotypic values associated with each germplasm in each study. The main tables are:
-
• OBSERVATION VARIABLES:
Metadata defining observation variable. An observation variable is the way a trait is recorded.
A trait can be observed qualitative and quantitatively and with different methods or scales.
Therefore, an observation variable is composed by the unique combination of one Trait, one Method and one Scale.
• METABOLITES:
Metadata associated with a metabolomics experiment. A metabolite is a special type of observation variable.
A metabolite is defined by the unique combination of one Trait, one analyte, a method, a retention time and / or mass to charge ratio,
the confidence scores (annotation and identification level) and the scale it was measured.
• OBSERVATIONS:
Observations are the experimental units of a study. They contain metadata associated with a macroscopic phenotyping experimental unit:
the study and the germplasm where the observation is taken for a given observation variable, the level (block, plot, plant) and replicate
at which observation is performed and information about the position of the plants in the field accordingly to the experimental design and its coordinates.
• SAMPLES:
Biological plant material collected in a study for molecular or microscopic phenotyping. Samples contain information about the study and
the germplasm (or the observation) where they were collected, the plant anatomical entity and developmental stage from which sample is collected and how sample was obtained.
• PHENOTYPIC DATA:
Datasets recording the value of an observation variable or a metabolite in a given observation or sample.
What is the genotyping module?
The genotyping module stores the genetic information related to germplasm (variant sets) and the metadata associated to it, including genotyping platforms and the markers genotyped by each platform. HarnesstomDB V1.0 only can store short DNA variants, SNPs and PCR based makers. The main tables are:
-
• GENOTYPING PLATFORMS:
A genotyping platform in HarnesstomDB is defined as a panel of markers mapped to a specific version of a reference
genome and obtained using closed (SNP-arrays) or semi-open (GBS, RAD-seq, DArTseq..) genotyping technologies.
• MARKERS:
collection of genetic landmarks with a known physical position on a chromosome created using a genotyping platform.
• GENOTYPIC VARIANT SETS METADATA:
Variant sets are the genotyping value of a maker in a germplasm sample. This contains information related to the genotyping platform used
the method (filters and software) used to generate the variant set and if there is any publication associated to this variant set.
• GENOTYPIC VARIANT SET DATA:
Variant datasets recording the value of a marker in a given sample.
What is the variant catalogue module?
The variant catalogue contains comprehensive and curated information of published and non-published QTLs and GWAS variant. This module stores information related to QTLs and GWAS experiments and variant-trait association summary statistics. Information in this module can be uploaded only if core, germplasm, phenotyping and genotyping data regarding to this experiment is up-loaded in the database. The main tables are:
-
• QTL STUDIES:
Information about how QTL study was performed. Phenotypic and genetic data, mapping population, methods and statistic cut-off.
It can store metadata for single environment QTL study, multi-environment study or epistasis studies
• QTL VARIANTS:
QTLs associated to a trait and the summary of statistics resulting from a QTL study.
• QTL EPISTASIS:
Interactions among multiple QTL affecting the same trait and the statistics resulting from a QTL study.
• GWAS STUDY:
Information about how GWAS study was performed. Phenotypic and genetic data, GWAS panel population, methods and statistic cut-off.
It can store metadata for single environment GWAS study and multi-environment studies.
• GWAS VARIANTS:
SNPs associated to a trait and the summary of statistics resulting from GWAS study.
Definitions
The most basic concepts and data standards terms used on HarnesstomDB are:
-
• Accession: a group of related plant material from a single species which is collected at one time from a specific location. Each accession is identified uniquely by the institute that maintains it and the original accession number from passport descriptor.
• Accession attribute: any heritable information inherent to the accession relevant for breeding.
• Analyte: A chemical compound defined by a Mass to charge ratio or retention time, its name, an annotation and identification confidence Level, and the method used to measure it.
• Collecting mission: trips aimed at the collecting the still existing gene resources of plants in a region.
• Collection: Subset of germplasms selected by different criteria.
• Contacts: persons related to the project (program leader, submitter, researcher…)
• Crops: the common crop name associated with the data (a crop includes the cultivated species and its wild relatives).
• Genotyping platform: a panel of markers mapped to a specific version of a reference genome and obtained using genotyping technologies.
• Germplasm: the identifier of an accession, provided by a specific institute, in a program.
• Location: the place where the experiment took place.
• Markers: genetic landmark with a known physical position on a chromosome created using a genotyping platform.
• Metabolite: variable composed by the unique combination of one metabolic trait plus an analyte and one scale.
• Observation variable: Unique combination of one trait, one method and one scale.
• Observations: define the experimental units where trait variables are recorded. Are defined by the unique combination of one study, one germplasm, the experimental unit in the experimental design.
• Parameter: any constant experimental condition used in the study different from the experimental factor or treatment. Is composed by a factor and its units.
• Pedigree: a germplasm resulting from a cross and a breeding generation. Define the genetic relationship between germplasm, their parents and progeny, as result of breeding crosses.
• Program: research projects with defined aims associated with a crop. They can exist at various scales (for example, they could encompass a grant-funded programme of work with trials and studies or a breeding program). A Program can contain multiple Trials.
• Samples: Biological plant material collected in a study for molecular or microscopic phenotyping.
• Study: experiment conducted at a single geographic location to answer the defined question in a trial.
• Study factor: The experimental factor or treatment whose effect is studied.
• Synonyms: Alternative names or IDs used to reference the accession in different projects, GenBanks or institutes.
• Trial: single or multiple studies (e.g. multi location international trials) conducted to answer a particular biological question in a frame of a program.
Controlled vocabulary
To harmonize entity attributes covering different key aspects associated to the metadata, and ensure HarnesstomDB interoperability with other databases, attributes of specific tables use ontologies, ISO standards and custom controlled vocabularies. Custom controlled were defined when no standard or ontology was available. To facilitate submission, controlled vocabulary is provided in drop-down lists where possible. Some ontologies were common to all modules and other specific for each module. The ontologies provided in Harnesstom are:
General ontologies Experimental core metadata Germplasm module- Collecting/acquisition source
- Biological Status of the accession
- Multilateral System (MLS) Status
- Taxonomy
- Storage type
- Attribute category
- Attribute
- Breeding method
- Generation
- Anatomical Entity
- Developmental Stage
- Trait
- Scale Category
- Observation Variable Method
- Metabolic trait
- Identification Level
- Annotation Level
- Metabolite class
- Analyte health and Flavour class
- Variant association Software
- Trait pre-processing
- QTL Method
- QTL Statistic
- Ci criteria
- Threshold Method
- GWAS Model
- Kinship algorithm
- Structure method
- Genetic testing model
- Allelic effect estimator
- GWAS Statistical significance test
HarnesstomDB Standards
Numbers and dates
Thousands without any separator, comma or dot. Example: 1000 Decimal number is represented by a dot. Example: 0.1 Missing data should be indicated by NA Date should be in the format dd/MM/yyyy. Example: 29/11/2022.
Geographical coordinates:Latitude: Expressed in two degrees in decimal format (±DD.DDDD). Example: +41.2587 Longitude: Expressed in two degrees in decimal format (±DD.DDDD). Example: -7.7809 Altitude: Its specified metres [m] value (±AAAA.AAA). Example: 162.